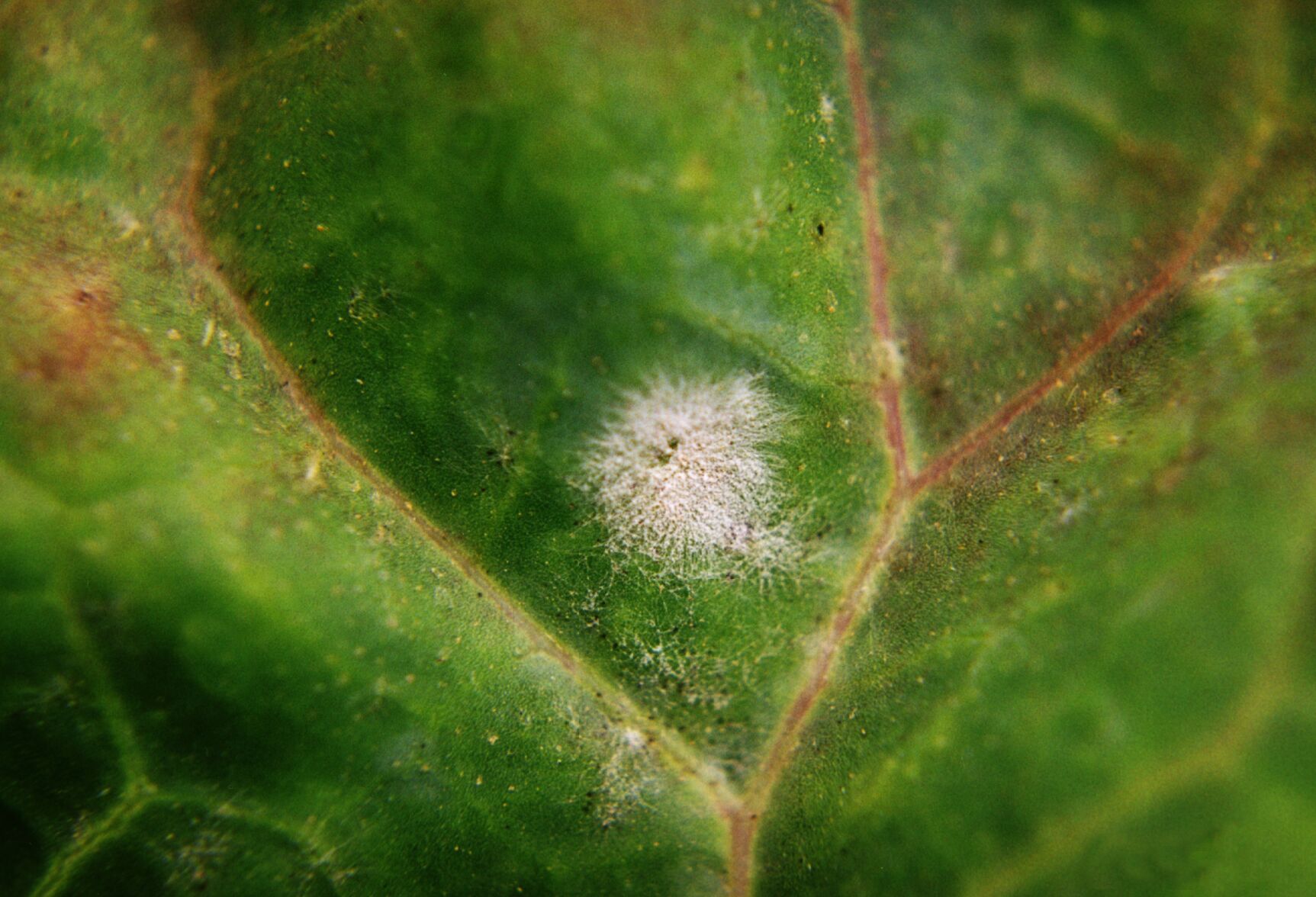
Powdery mildew is a common fungal disease which presents as white powdery spots on the leaves of plants. Left unchecked, the fungus will spread until it encompasses the whole crop, the quality of the crop spoils and its yield is reduced.
What is powdery mildew?
A common fungal disease that affects many different plants and crops, powdery mildew is caused by different fungi.
This foliar disease earned its name from the distinctive white or greyish powder-like coating it leaves on infected plant surfaces. This makes it one of the easiest plant diseases to spot.
Without safe, sustainable and effective options to protect different crops, pests and diseases will render the harvest inedible and unsellable. It is estimated that farmers worldwide lose up to 23 percent of their crops to fungal diseases such as powdery mildew each year, with a further 20 percent then lost post-harvest.
In the five most important calorie crops – rice, wheat, corn, soybeans and potatoes – fungal infections have been estimated to cause yield losses that could feed at least 600 million people every day for a year.
Scientists say these effects will likely worsen under climate change. Warmer temperatures and changing rainfall patterns expand the footprint where disease-causing fungi can occur and thrive, and warmer temperatures create more opportunities for them to evolve.
What are the typical symptoms of powdery mildew?
Typical symptoms of powdery mildew across vegetables, field crops and ornamentals include:
- white, powdery spots on leaves, stems, and sometimes fruits;
- yellowing and curling of leaves.
The infection can result in stunted growth, premature leaf drop, and reduced quality and yield.
Severe mildew damage reduces leaf growth, aesthetic value of plants, photosynthetic efficiency and thereby plant growth. Plants can be severely stunted if they are heavily infected early in the growing season. When the environmental conditions are favourable, the affected leaves may fall prematurely.
Symptoms can vary slightly depending on the crop, the specific fungal species and environmental conditions. Early detection is key for effective management of powdery mildew across all crops.

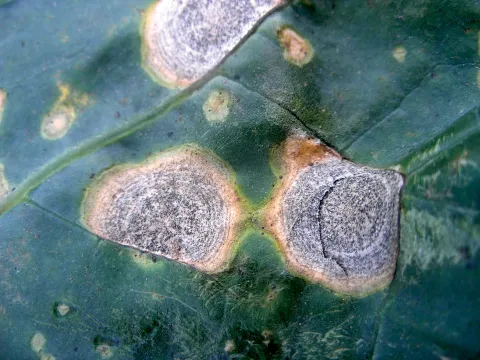
Powdery mildew disease on a cabbage leaf
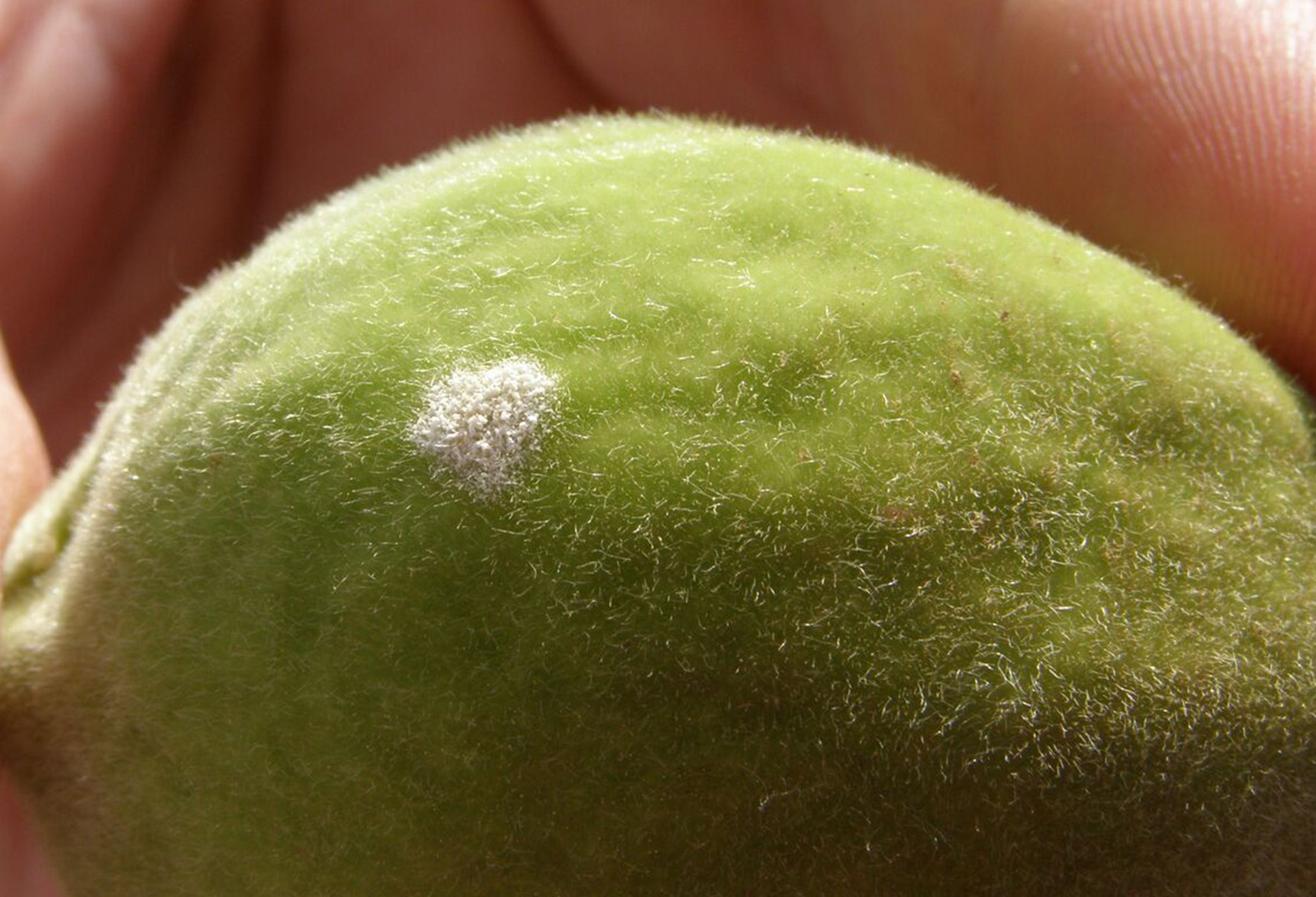

Powdery mildew disease on a peach
Powdery mildew treatment
With diseases often evolving faster than the ability to contain or control them in crops, continuing to develop innovative solutions for growers to use is important for addressing widespread issues, such as powdery mildew.
Farmers around the world need to grow higher yields of healthy, sustainable crops to feed a growing population in increasingly unpredictable conditions with a limited number of solutions to keep their crops healthy and disease-free.
New technology in crop protection provides an effective tool to combat crop diseases like powdery mildew, enhancing crop yields and sustainability.
The groundbreaking MIRAVIS™ Duo fungicide from Syngenta gives excellent control of powdery mildew. The product's increased defense against pests and diseases, coupled with the higher yield capabilities are thanks to the market leading ADEPIDYN® technology (trademark for the active ingredient pydiflumetofen).
The next-generation fungicide is based on a unique molecule that protects multiple types of crops against many different diseases. Long-lasting and potent, it has a low application rate but is far more effective than conventional products on the market.
This efficient fungicide means crops are better able to withstand disease pressures, meaning when they are harvested, they are healthier, and yields are higher. That means growers can achieve better prices for their crops, offering economic security and peace of mind.
From the laboratory to the field
When it comes to developing a new crop protection tool for farmers, everything starts with a single molecule. Through years of rigorous testing and refining, a promising candidate emerges in the laboratory.

How can powdery mildew be prevented?
Growers can use different strategies to help prevent powdery mildew infection in their crops. Cultural practices, such as improved spacing between plants for better air circulation, avoiding overhead irrigation, removing any infected debris, crop rotation, and strategic pruning, can create an environment less favorable to fungal growth.
Integrated disease management also helps support healthy plant growth. This includes regular monitoring, utilizing disease forecasting models, and implementing a range of interventions which may include organic fungicides like sulfur, biological control agents such as Bacillus subtilis, and targeted chemical fungicide applications when necessary.
Choosing resistant varieties can help growers reduce fungicide use, lower costs, decrease environmental impact, and stabilize yields – for example, powdery mildew-resistant cucumbers and wheat varieties with Pm genes.
New approaches, such as UV-C light treatments in greenhouses, silicon-based fertilizers to enhance plant defences, and companion planting with naturally fungicidal plants, also help to boost a plant’s defenses.
Environmental management, especially in controlled growing environments, is important. This means monitoring humidity levels, optimizing plant nutrition, and managing irrigation.
Ultimately, a holistic and flexible approach to the prevention and management of powdery mildew (including cultural practices, resistant varieties, biological controls and targeted fungicide use) means growers can tailor their approach depending on their crops and locality.
To prevent a disease developing resistance it is important to alternate between different active ingredients. Growers should pay attention to the mode of action the product has.
Rotation of products is a key strategy but it’s important those products have different FRAC codes, as this can reduce further resistance development. Ensure your program takes this into account.
Syngenta solutions for powdery mildew
Fungicides
-
ADEPIDYN® technology
ADEPIDYN® technology (the trademark for active ingredient in the MIRAVIS® brand) is a next-generation fungicide based on a unique molecule which can be used across multiple crops and against many different diseases – including powdery mildew. It is potent, long-lasting and has a low application rate, and replaces many less effective conventional products.
-
CIDELY® Top
CIDELY® Top contains difenoconazole and cyflufenamid, two active ingredients effective against powdery mildew in a range of horticultural crops.
-
TOPAS® 100 EC
TOPAS® 100 EC contains penconazole for the control of powdery mildew in apples, crab apple, pears, blackcurrants, redcurrants, grapes, outdoor and protected strawberries.
Biologicals
-
RAVIBIS™
RAVIBIS™ - For growers and producers of apples, strawberries and vegetable crops looking for control of powdery mildew and scab, RAVIBIS™ offers a biological control solution that is simple, reliable and sustainable. RAVIBIS™ consists of sodium hydrogen carbonate which has a preventive and curative effect on scab and powdery mildew.
-
TAEGRO®
TAEGRO® Is a biofungicide, a microorganism-based fungicide for the suppression of foliar diseases in a range of crops. TAEGRO® is a microorganism-based fungicide, approved for use in organic systems, suppressing diseases on ornamental crop production, nursery fruit trees, grapevines, strawberry and other edible crops (see label and EAMU for full details) grown outdoor or under temporary/permanent protection.